LSUMn calculates the sum of the last n datapoints of a specified variable.
SYNTAX:
LSUMn(Cx, optional Time Increment)
where :
Cx is a conditional variable x
n is the number of values to total
Time Increment Optional - specifies the source variables (Cx) Frequency when the Source Variable (CX) and target variable's (i.e. the variable being calculated) frequencies do not match.
NOTES:
The data points do not need to be on consecutive days
Calculates every day that it can find n values to sum, searching up to one year (366 days) backward
Does not calculate if n values are not available
The result is stored based on target variables frequency:
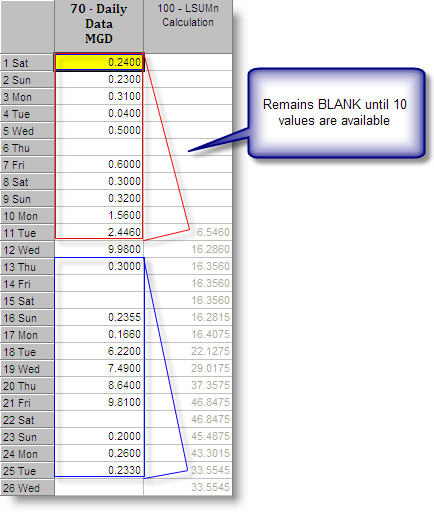
EXAMPLE 1: Get sum of last 10 values from a daily variable
Source variable (70) is set to Daily and Target variable (100) is also set to Daily. Because both the Source and Target variables are the same (Daily), the time increment BYDAY will be used.
V100 = LSUM10(C70)
Variable 100 will be the total sum of the last 10 values of variable 70:
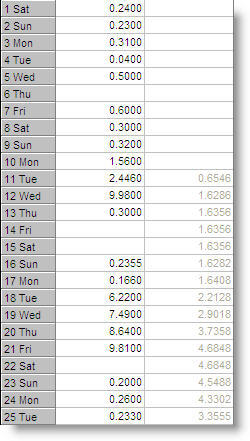
Example 2: Averaging with LSUMn
V100 = LSUM10(C70)/10
This divides the sum by the total number of values (10), which returns the average of the last 10 values:
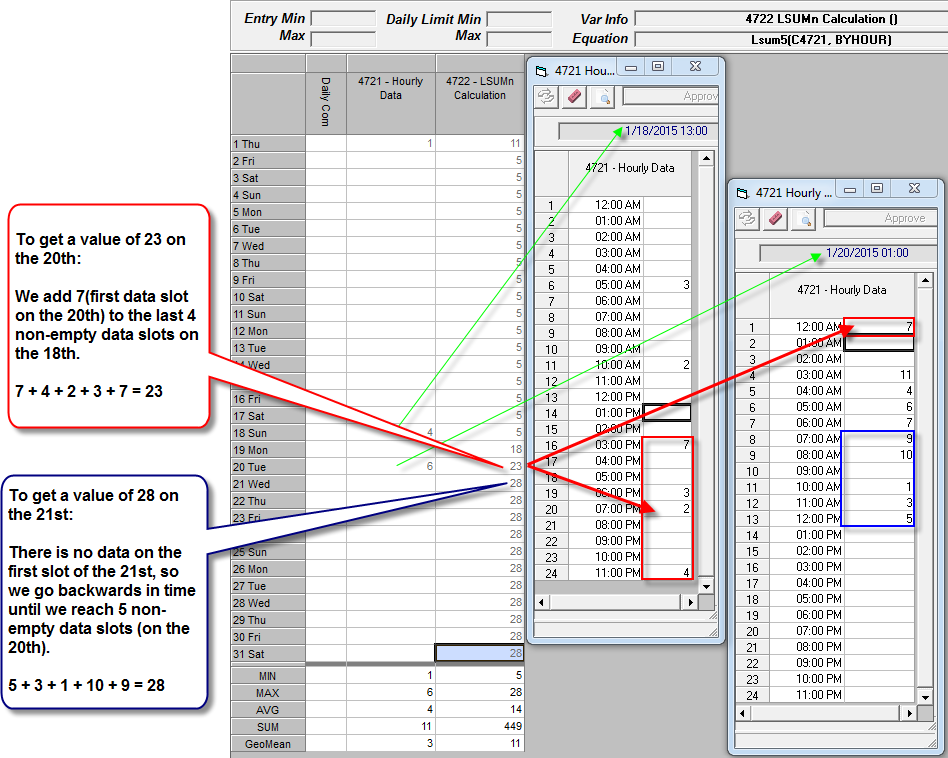
Example 3: Get sum of last 10 values from an Hourly variable into a Daily Calculation.
Source variable (70) is set to Hourly and Target variable (100) is set to Daily.
V70 - Is a hourly parameter
V100 - Is a daily calculation
V100 = LSUM5(V70,BYHOUR)
Note: You MUST specify the Time Increment (BYHOUR) that matches the source variables frequency (IE the source variable V4721 is Hourly, therefore we specify BYHOUR) in order for the function to return the correct value.
When calculating daily detail variables, the program will start on the first slot of the day being calculated and add the first 5 non-empty values going backward in time for up to a year. See screenshot below
See: Working with Daily Detail Variables in Calculations.