YAVG returns the Year-To-Date average of a specified variable, Cx, and stores the corresponding value each day.
SYNTAX:
YAVG(Cx, optional Time Increment)
where :
Cx is a conditional variable x
Time Increment Optional - specifies the source variables (Cx) Frequency when the Source Variable (CX) and target variable's (i.e. the variable being calculated) frequencies do not match.
NOTES:
The variable being averaged must be specified as a Conditional Variable (use "C" instead of "V")
Care must be taken to keep this calculation up to date. For example, if today were June 15th and for some reason you edited a value in the input variable, Cx, for February 14th; then you recalculated the month of June only. The only values that have been updated to reflect the new value in February are those in June. You must recalculate the variable containing this function from February 14th to the current date to update all values in between accordingly.
The result is stored based on target variables frequency:
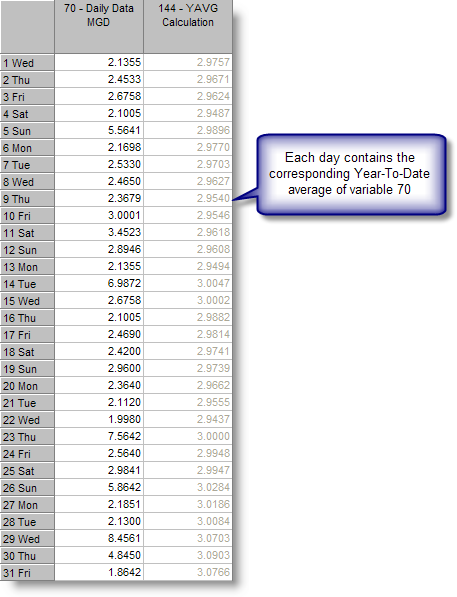
EXAMPLE 1: Return the Year-To-Date average from a variable
Source variable (70) is set to Daily and Target variable (144) is also set to Daily. Because both the Source and Target variables are the same (Daily), the time increment BYDAY will be used.
V144 = YAVG(C70)
Variable 144 will have a daily value that is the Year-To-Date average of variable 70:
EXAMPLE 2: Return the Year-To-Date average from an Hourly variable into a Daily Calculation.
Source variable (70) is set to Hourly and Target variable (144) is set to Daily.
V70 - Is a hourly parameter
V144 - Is a daily calculation
V144 = YAVG(V70,BYHOUR)
Note: You MUST specify the Time Increment (BYHOUR) that matches the source variables frequency (IE the source variable V70 is Hourly, therefore we specify BYHOUR) in order for the function to return the correct value.
See: Working with Daily Detail Variables in Calculations.