GMED returns an aggregate median statistics for an input variable.
The number of values that are aggregated is determined based on the frequency of the input variable.
SYNTAX:
GMED(Cx)
where :
Cx is a input conditional variable x.
NOTES:
The input variable frequency should be less than the result variable frequency. It makes sense to aggregate 5 one-minutely values into a 1 five-minute variable, but not the other way around.
EXAMPLE:
V6041 = GMED(C6000)
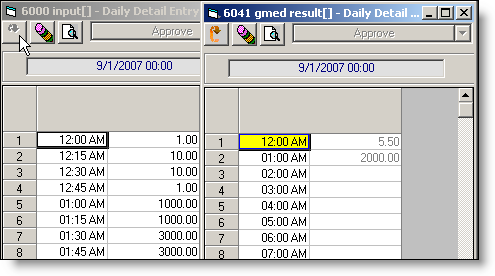
where V6000 is a 15 minute variable, and V6041 is an hourly variable.
Example with MDL Rules:
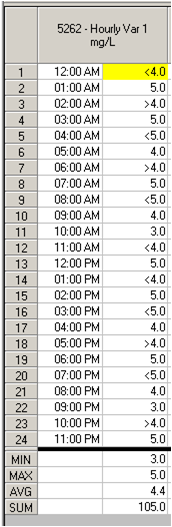
V = GMED(C5262)
On calculated variables, it is possible to elect to cascade MDL rules or not. Below is an example of cascading MOST frequent MDL symbol, ALL MDL symbols, and NONE or no MDL symbols. For this example, our data is in an hourly variable (C5262) and our calculated variables are all 4 hour variables.
V9661 - Most Frequent MDL Symbol
V9662 - All MDL Symbols
V9663 - No MDL Symbols

Here is the data, in variable 5262, that the calculated variable above is using: