Supported variable configurations for the Hach WIMS Direct Server-Side Interface to Charleston's SCADA system.
To configure a variable to hold values from this SCADA, select Edit/View Variables in the client and select the Interface tab.
Then click Interface To radio button. The drop down box next to the option is now enabled, click the drop down arrow and choose the name given when configuring the interface.

Now you are ready to configure a tag from the SCADA system. The Table name, Tag name and a statistic are all mandatory.

Clicking on the question mark will bring up the following screen:

The following image shows the screen with all data3 selected. Here is a breakdown of the functions of the controls on the screen:
- Select the table that holds the data. This drop down lists all tables in the database.
- This drop down allows the user to select the field that holds the time data.
When the table is selected this drop down is filled with the fields in that table and if a field has a name that contains the word "time" in it, it is selected automatically (though the user can select another if he wishes).
- This drop down also has a list of fields from the selected table and allows the user to select field holding the actual data.
When this field is selected a query is performed on the table and the top 100 records from that field are shows in the list below it. If you check the Filter Sample Data by Selected Tag you will see values for that tag only.
- This drop down also has a list of the fields from the selected table and if one of the fields is named "TagName" it is selected automatically.
The distinct values from this table are shown in the list below it.
- If this check box is checked then the sample data values shown below it are only values for the tag selected on the left.
If the Data Field Values list is empty and this check box is checked then you haven't selected a tag from the list to the left.
- Here is where you can select the Tag for the variable.
- to create a tag value for the variable you must have the following selections made: Table Name (1), Date/Time (2), Data Field Name (3), Tag Field Name (4) and the Tag value selected (6).
This shows the text that will be copied into the Tag field in the Interface tab of the variable setup screen.

This screen uses the user entered database connection information from the Add/Edit Server-side Interface screen (System Setup | System Tables | Entire System | Server-Side Interface Setup menu items. There is a description here). The interface must upload it's configuration data before you can configure the database connection information on the above screens. The below image shows data in the TAG field that has been selected from the Browser screen.
In the below image you can also see data in the Filter Tag field that was entered using the same selection method (though the "?" button next to that text field was pressed).

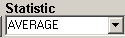 This is a listing of all the statistics supported by this interface. This includes the following statistics for a specified time period:
This is a listing of all the statistics supported by this interface. This includes the following statistics for a specified time period:
| AVERAGE |
Take the average of the data points in the time period |
| TOTAL |
Take the sum total of all values in the specified time period |
| MINIMUM |
Take the minimum value in the specified time period |
| MAXIMUM |
Take the maximum value in the specified time period. |
| FIRST |
Take the first reading in the time period |
| LAST |
Take the last reading in the time period. |
| DIFF |
This statistic calculates the difference between the first value and the last value for the period requested (i.e., if the variable is defined as an hourly variable, DIFF will get the first and last values for each hour and subtract them) |
| RANGE |
This calculates the range of your values for a specified period. It calculates the difference between the minimum and maximum values for the period requested. |
| INVENTORY |
Returns the total use based on a tank level signal. For example, the level is 10 feet at midnight and slowly goes down to 2 feet at 2:00PM then gets filled to 15 feet and slowly goes down to 8 feet at midnight. The inventory function would return 15 |
| TIMEGT(n) |
Returns the number of minutes the value was greater than n (i.e. value specified in parentheses). Example TIMEGT(5), returns number of minutes tag > 5. |
| TIMELT(n) |
Returns the number of minutes the value was less than n (i.e. value specified in parentheses). Example TIMELT(5), returns number of minutes tag < 5. |
| TIMEEQ(n) |
Returns the number of minutes the value was equal to n (i.e. value specified in parentheses). Example TIMEEQ(1), returns number of minutes tag equals 1. |
| COUNT |
This will count the number of data points for a given tag over a specified period of time. |
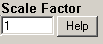 This is the value to multiply the result by when using parameter variable types. Commonly used to convert from one unit base to another. For example to convert gallons per minute (GPM) to gallons per day (GPD), set the scale factor to 1440 (1440 minutes per day).
This is the value to multiply the result by when using parameter variable types. Commonly used to convert from one unit base to another. For example to convert gallons per minute (GPM) to gallons per day (GPD), set the scale factor to 1440 (1440 minutes per day).
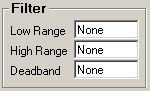 All three fields must have numeric values or the word None (as shown). The Low Range and High Range will crop data from the source. For example to eliminate negative numbers from a particular tag, set the Low Range to 0 (zero) - this will get any values equal to or greater than 0 (zero). The Deadband is used for the statistic Inventory and will eliminate noise levels up to the value specified. For example, if you enter .5 next to Deadband, any value change of .5 or less, will be ignored.
All three fields must have numeric values or the word None (as shown). The Low Range and High Range will crop data from the source. For example to eliminate negative numbers from a particular tag, set the Low Range to 0 (zero) - this will get any values equal to or greater than 0 (zero). The Deadband is used for the statistic Inventory and will eliminate noise levels up to the value specified. For example, if you enter .5 next to Deadband, any value change of .5 or less, will be ignored.
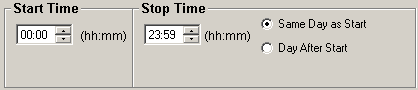
- Start Time will set the beginning of the time slot for this variable.
- Stop Time will set the ending time for the time slot.
- Same Day as Start is only used by daily variables and it means the stop time is on the same day as the start time.
- Day After Start is also only used by daily variables and it means the stop time is a day after the start time.
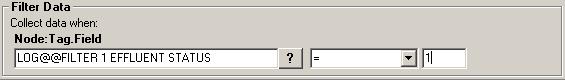
- Node Tag Field is the signal tag to filter by from the Narrow Format OLEDB. You can find tag names using the ? the same way you found the signal tag above.
- The second field is the filter operator drop down. This includes the following:
| SYMBOL |
DESCRIPTION |
| < |
Less than, true if the value returned is less than the filter value |
| > |
Greater than, true if the value returned is greater than the filter value |
| = |
Equal to, true if the value returned is equal to the filter value |
| <= |
Less than or equal to, true if the value returned is less than or equal to the filter value |
| >= |
Greater than or equal to, true if the value returned is greater than or equal to the filter value |
| <> |
Not equal, true if the value returned is not equal to the filter value |
| Cycles To |
Summarize values based on statistic when the Filter Tag changes to Filter Value. |
| ACT(n) |
Summarize values based on statistic looking at data that is n minutes after the Filter Tag changes to the Filter Value. |
| BCT(n) |
Summarize values based on statistic looking at data that is n minutes before the Filter Tag changes to the Filter Value. |
| GOES>(n) |
Summarize values based on statistic looking at data that is offset n minutes from when the Filter Tag goes above the Filter Value. N of Zero (0) means get data in the same minute, 1 means 1 minute after, -2 means 2 minutes before. |
| GOES<(n) |
Summarize values based on statistic looking at data that is offset n minutes from when the Filter Tag goes below the Filter Value. N of Zero (0) means get data in the same minute, 1 means 1 minute after, -2 means 2 minutes before. |
- The last field is the filter value. The value returned from the filter tag is compared to this value.