Supported variable configurations for the Hach WIMS Direct Server-Side Interface to WIMS Cache. Before continuing, ensure you have configured this interface, see Step-by-Step Instructions on How to Configure Interfaces.
To configure a variable to hold values from the source, select System Setup > Edit/View Variables in the Hach WIMS Client and select the Interface tab.
Then click Interface To radio button. The drop down box next to the option is now enabled, click the drop down arrow and choose the WIMS Cache interface name (name given when configuring the interface).
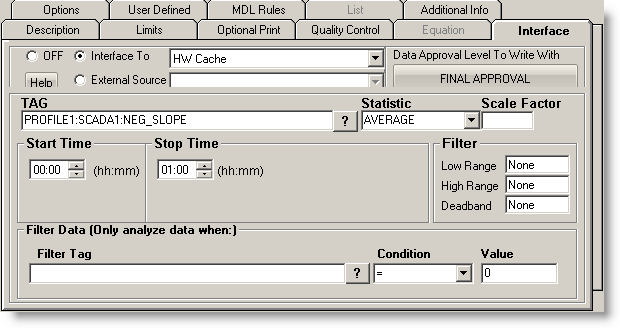
Now you are ready to configure a signal tag from the Trihedral VTS HMI Historian. The Tag name and a statistic are all that are mandatory.
-
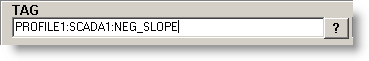 This is the tag name. The ? symbol (question mark) will allow you to browse the Historian database for tag names. The TAG has the following format:
This is the tag name. The ? symbol (question mark) will allow you to browse the Historian database for tag names. The TAG has the following format:
Profile:Server:Tag
- Profile: this is the Profile Name for the Target source in the Dispatcher when using Hach WIMS Cache type
The value can also be found in the UniqueName field of the Profile table of the Hach WIMS Cache database.
- Server: this is the server name of source data and can be found in the OPSDATAXML revision 3 data files that the Dispatcher imported data from. The server name is found in the s_id field of these XML files.
The value can also be found in the Name field of the Server table of the Hach WIMS Cache database.
- Tag: this is the tag name that the source data uses to identify components in the treatment plant and can be found in the OPSDATAXML data files that the Dispatcher imported data from. The tag name is found in the t_id field in these XML files.
The value can also be found in the Tag field of the Tag table of the Hach WIMS Cache database.
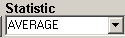 This is a listing of all the statistics supported by this interface. This includes the following statistics for a specified time period:
This is a listing of all the statistics supported by this interface. This includes the following statistics for a specified time period:
NOTE: All statistics return a BLANK when no data is found. Be aware that when data is filtered, it is possible to return a BLANK.
|
STATISTIC |
DESCRIPTION |
|
AVERAGE |
Take the average of the data points |
|
TOTAL |
Take the sum total of all values |
|
MINIMUM |
Get the minimum value |
|
MAXIMUM |
Get the maximum value |
|
FIRST |
Get the first value |
|
LAST |
Get the last value |
|
DIFF |
Calculate the difference between the first and last values. If the first value is larger than the second then it will perform the following calculation: (10 ^ (Ceil(LOG(first_value) / LOG(10)))) - first_value + last_value
Ceil will cause the value to round up |
|
RANGE |
Calculate the absolute value of the difference between the minimum and maximum values |
|
INVENTORY |
Return the total use based on a tank level signal. For example, the level is 10 feet at midnight and slowly goes down to 2 feet at 2:00 PM, then gets filled to 15 feet and slowly goes down to 8 feet at midnight. The inventory function would return ((10 - 2) + (15 - 8)) = 15. |
An example of a query for this interface:
SELECT Avg(r.reading) FROM profile p, server s, tag t, reading r WHERE p.id = s.profileFK AND s.ID = t.serverFK AND t.ID = r.tagFK AND p.uniqueName = 'PROFILE1' AND t.tag = 'NEG_SLOPE' AND r.dateStamp >= '2010-08-12 07:00:00' AND r.dateStamp < '2010-08-13 07:00:00'
This is getting the Average reading of NEG_SLOPE from PROFILE1. The data returned will be from midnight of 12 Aug, 2010 to midnight 13 Aug, 2010 - NOTE: the time is for UTC date (07:00:00, seven hours difference) which will be changed to local time once the average is calculated.
The records returned from the query are then loaded into an array and the statistic is calculated.
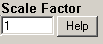 This is the value to multiply the result by when using parameter variable types. Commonly used to convert from one unit base to another. For example to convert gallons per minute (GPM) to gallons per day (GPD), set the scale factor to 1440 (1440 minutes per day).
This is the value to multiply the result by when using parameter variable types. Commonly used to convert from one unit base to another. For example to convert gallons per minute (GPM) to gallons per day (GPD), set the scale factor to 1440 (1440 minutes per day).
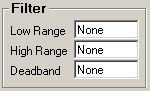 All three fields must have numeric values or the word None (as shown). The Low Range and High Range will crop data from the source. For example to eliminate negative numbers from a particular tag, set the Low Range to 0 (zero) - this will get any values equal to or greater than 0 (zero). The Deadband is used for the statistic Inventory and will elliminate noise levels up to the value specified. For example, if you enter .5 next to Deadband, any value change of .5 or less, will be ignored.
All three fields must have numeric values or the word None (as shown). The Low Range and High Range will crop data from the source. For example to eliminate negative numbers from a particular tag, set the Low Range to 0 (zero) - this will get any values equal to or greater than 0 (zero). The Deadband is used for the statistic Inventory and will elliminate noise levels up to the value specified. For example, if you enter .5 next to Deadband, any value change of .5 or less, will be ignored.
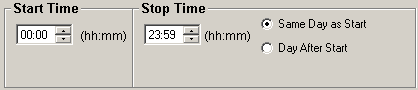
- Start Time will set the beginning of the time slot for this variable.
- Stop Time will set the ending time for the time slot.
- Same Day as Start is only used by daily variables and it means the stop time is on the same day as the start time.
- Day After Start is also only used by daily variables and it means the stop time is a day after the start time.
-
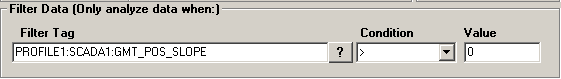 Filter Tag is used to filter source data by another tags' value. You can find tag names using the ? the same way you found the signal tag above.
Filter Tag is used to filter source data by another tags' value. You can find tag names using the ? the same way you found the signal tag above.
- The second field is the filter operator drop down. This includes the following:
|
SYMBOL |
DESCRIPTION |
| < |
Less than, true if the value returned is less than the filter value |
| > |
Greater than, true if the value returned is greater than the filter value |
| = |
Equal to, true if the value returned is equal to the filter value |
| <= |
Less than or equal to, true if the value returned is less than or equal to the filter value |
| >= |
Greater than or equal to, true if the value returned is greater than or equal to the filter vaue |
| <> |
Not equal, true if the value returned is not equal to the filter value |
- The last field is the filter value. The value returned from the filter tag is compared to this value.