MOVn returns an n day moving average of a specified variable. If daily detail variables are used returns the n "slot" moving average.
SYNTAX:
MOVn(Cx)
where :
Cx is a conditional variable x
n specifies the number of days to calculate the average. If daily detail variables are used returns the n "slot" moving average (ie for an hourly variable would specify the number of hours, for a 15 minute varaible the number of 15 minute slots.
NOTES:
n MUST be between 1 and 500. Spans larger than 500 days will not calculate
In general, a conditional variable should be used (Cx). The result will include the current date in the calculation.
This function requires the target and source variable frequencies to match. E.g. Hourly target variable = Hourly source variable, 5-Minute Target variable = 5-Minute Source Variable. If the frequencies do not match, the function will return incorrect values.
EXAMPLE #1: Calculate the 14 day moving average of a daily variable
V114 = MOV14(C71)
Each day, variable 114 will contain a 14 day moving average of the data in variable 71

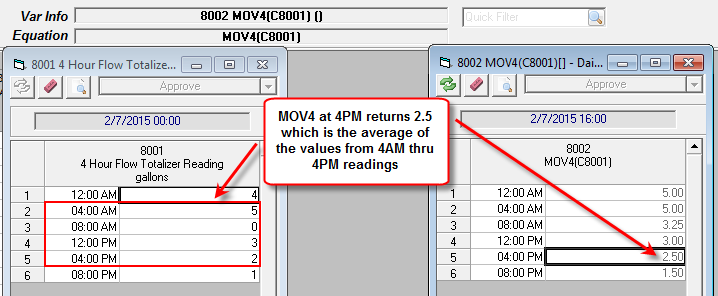
EXAMPLE #2: Calculate a 16 hour moving average of a 4 Hour variable
V8001 is a 4 Hour Parameter variable
V8802 is a 4 Hour Calculated variable
V8002 = MOV4(V8001)
EXAMPLE #3: Calculate the 7 day moving avearage from an hourly variable into a daily calculation.
Since we are mixing variable frequencies the MOVn function will not work. We need to use the advanced math toolbox function GETAVG.
V2 is an hourly parameter
V3 is a daily calculation
V3 = GETAVG(C2,#MM/-6 TO EOD, BYHOUR)
When calculating Jan 7th, 2015 this calc would include data from Jan 1st 00:00 thru the last hourly slot of Jan 7th, 2015 (i.e. data for Jan 7th, 11PM slot will be included).